Ransomware Prevention: Protecting Against the #1 Source of Infection
Adrien Gendre
—May 11, 2023
—4 min read

Seven in 10 businesses were the victim of a ransomware attack in 2022, according to a global survey by Statista, the highest reported rate ever. Invasive and difficult to detect, ransomware attacks are a top cyberthreat, costing businesses on average $4.5 million (USD) globally. For small-to-midsized businesses (SMBs) and managed service providers (MSP), ransomware prevention remains vital not only to cybersecurity and business continuity, but survival.
While hackers use multiple techniques for deploying ransomware, phishing attacks account for the #1 distribution method and should warrant top consideration for your preventative measures.
In this article, we examine the threat of phishing-based ransomware attacks and the four measures you need to prevent compromise.
Phishing: the most common method of ransomware infection
Phishing requires less technical skill from hackers than other ransomware attack methods—such as exploiting Remote Desk Protocol (RDP) or software vulnerabilities.
In ransomware attacks, phishing emails may contain malicious attachments that download and infect a user’s computer at the time of click. These emails may also impersonate trusted brands to trick users into clicking links that deliver the malicious payload.
Alternatively, phishing campaigns may send victims to a phishing webpage for credential harvesting and account takeover. Hackers can then use the access to infect an entire network with ransomware through subsequent phishing emails, lateral movement, privilege escalation, or other techniques.
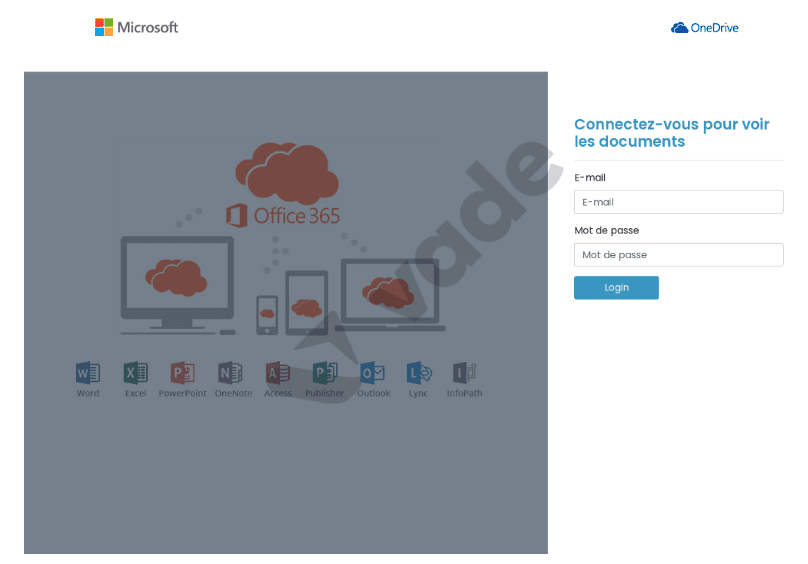
Phishing page detected by Vade impersonating Microsoft
Ransomware prevention: How to keep your organization and clients protected
To prevent ransomware attacks caused by phishing, your organization needs the ability to detect, identify, and remediate all email-borne threats, including those not yet seen in the wild and originating from external or internal sources. This comprehensive protection calls for supplementing native security tools like Exchange Online Protection (EOP) with four email security solutions.
1. AI filter engine
To prevent cyberthreats from reaching your users, you need an integrated and intelligent AI filter engine. This engine analyzes emails, attachments, and webpages to identify the behaviors and anomalies used in phishing, spear phishing, and malware attacks, including ransomware. It acts as the first line of defense against incoming threats, as well as a continual layer of protection for threats that may originate from or transit your network.
Still, not all AI engines are created equal. To optimize accuracy and precision, look for solutions that possess the following features:
- Multifaceted algorithms. To protect against all forms of email-borne threats, you need solutions that use Machine Learning, Computer Vision, and Natural Language Processing Machine Learning analyzes email attributes and files to identify suspicious behaviors characteristic of all email-borne threats. Computer Vision analyzes images to detect image-based threats. And Natural Language Processing identifies the subtle grammatical patterns, word choices, and phrasing used by text-based threats.
- Data. The predictive capabilities of AI depend on a significant amount of data. The more data it can learn from, the more it can recognize the patterns and behaviors needed to block inbound or outbound threats. That’s why you should look for solutions that draw from a large, current, and representative dataset.
- Human intelligence. AI depends on data scientists to build its algorithms, cybersecurity analysts to ensure the quality of data it learns from, and users to report suspicious emails that may constitute new or emerging threats. All support the filtering accuracy of AI, so look for solutions that use each of them.
2. Incident response capabilities
Threat detection is only one function of cybersecurity. Incident response is another. Because no cybersecurity solution can detect 100% of threats, you need the ability to respond quickly to the security incidents that inevitably occur. Your effective and timely response requires features that optimize your ability to visualize and address security events in real-time. Those features include:
- Single pane of glass. Toggling between multiple interfaces or applications inhibits fast and timely response. Admins benefit from solutions that provide one dashboard for incident monitoring and response and enable them to quickly see what warrants attention. This means tools should organize and group reported threats by similarity and cluster them with similar, yet unreported emails.
- Remediation. When remediating security events, admins benefit from solutions that eliminate duplicative tasks and enhance efficiency. This means enabling them with both automated remediation and the ability to remediate all instances of a reported threat with one action.
RELATED CONTENT: Why Users Should Report Suspicious Emails, and What Happens When They Do
3. Threat intel and investigation tools
For effective threat detection and response, you also need tools that support threat intelligence and investigation. This enables you to coordinate response activities, cross-check threats, and more. The following features enable you to enhance your ability to capture new intelligence and analyze it:
- File deconstruction. Admins need the ability to gather intelligence about email files and attachments. This enables them to gather critical information for decision-making, cross checking threats, and accelerating response across endpoints and users. That’s why solutions should deconstruct files and attachments—all without exposing admins to risk.
- User-reported emails. User-reported intelligence is vital to strengthening AI algorithms. When it comes to incident response, providing admins with a simple, efficient way to triage and remediate user-reported emails ensures that admins can prevent or mitigate damage from threats that bypassed initial detection.
- Integrations. Effective incident response calls for coordinating threat intelligence across the essential cybersecurity tools that make up your stack. Your email security solution should integrate vital intelligence with your SIEM, SOAR, or XDR in real-time, and vice versa.
4. Phishing awareness training
Your users remain the top vulnerability in your attack surface, as human error represents the single greatest cause of data breaches. To improve user behavior, your email security solution should offer phishing awareness training with the following features:
- Time-sensitive administration. User awareness training should be administered based on need, not according to an annual requirement or the schedule of admins. To improve user behavior, you need training that is administered whenever users encounter an actual phishing threat. By grounding training in lived experience, you directly connect instruction with the behaviors that improve cybersecurity, while enhancing learning retention.
- Personalization. The most effective education adapts instruction to the learner’s unique circumstances. This is especially the case when it comes to email security. Rather than teaching with generic examples, your users need training that reflects the email communications and brands they regularly interact with. This also grounds their learning in a context so they can recognize, retain, and apply their training.
- Ongoing automation. Training administration should be automated continuously. This ensures that you can deliver timely and personalized education at scale, ensure users remain proficient at dealing with cyberthreats regardless of turnover and other organizational changes, and free admins to focus on other priorities.
Vade’s approach to phishing awareness training is to train users when they need it most: when they have interacted with a phishing email. Unlike phishing simulations, Vade for M365 triggers automatic phishing awareness training using examples of real phishing emails and webpages.
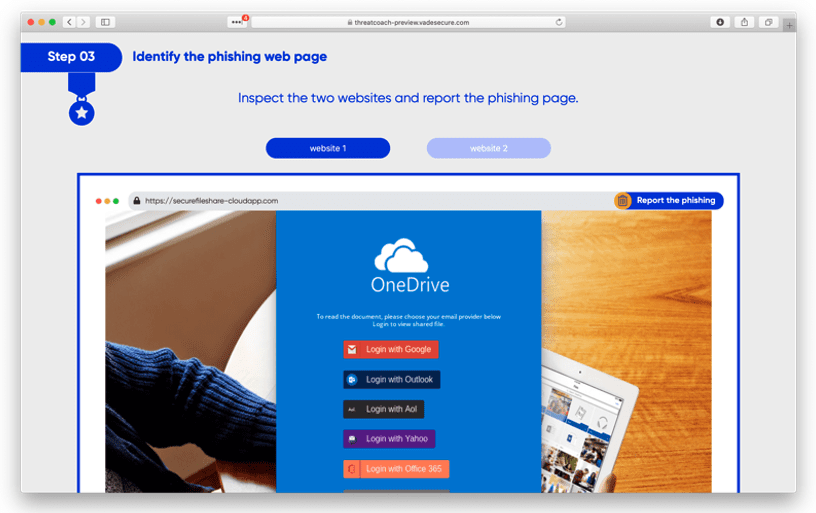
Vade Threat Coach™
The collection of new samples is programmatic, and new samples are added daily as new threats are detected.
Ransomware prevention calls for collaborative email security
Ransomware is an invasive and costly cyberthreat for organizations of all sizes. As phishing emails deploy the most ransomware attacks, organizations need collaborative email security. By layering protection onto native environments and tools, it enables you to support all necessary activities for ransomware prevention, including threat detection, response, investigation, and education.
Vade for M365 is the first collaborative email security solution for Microsoft 365. Integrated and low-touch, the solution provides AI-powered email security that catches the ransomware threats that Microsoft misses.








